- Home
- Treatments
- Surgery
Surgery
-
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Oral surgery is the field of dentistry that includes the diagnosis and surgical treatment of diseases, injuries and deformities involving both functional and aesthetic aspects of hard and soft tissues of the head, mouth, teeth, gums, jaws and neck.
Involves the removal of impacted teeth (sisos), apicoectomy, disorders of the temporomandibular joint, facial trauma, corrective surgery for deformities of the jaws, oral pathology or dental implants.
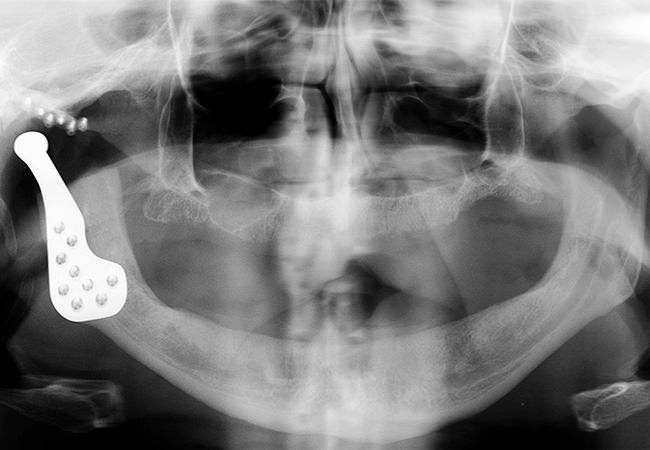
Reconstructive arthroplasty of the TMJ(with complete phrostesis)
Is indicated in cases with severely damaged joints due to birth defects, trauma or advanced osteoarthritis.
Cleft palate
Correspond to birth defects (occurring between the 4th and 10th week of gestation) characterized by gaps or discontinuity of the structures of the lip and / or palate, location and extent of variables
Cleft Palate - Before
Cleft Palate - After
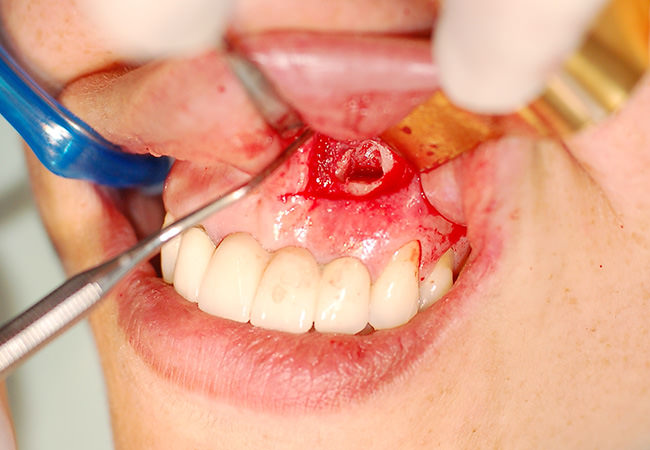
Apicoectomy
Some periapical lesions (cysts present in the root tip) can not resolve through the endodontic treatment (root canal), therefore requiring a curettage of the lesion, associated with an apicoectomy (removal of the final portion of the root).
Cysts and tumors
Cysts and tumors of the oral cavity are a broad group of lesions that should be identified and treated, preventing functional and aesthetic damage to the body. The problems can be congenital or appear during the development of organs such as teeth, bones and gums from irregularities and anomalies of tissues. Surgical treatment of these pathologies involve specific techniques for each type of lesion.
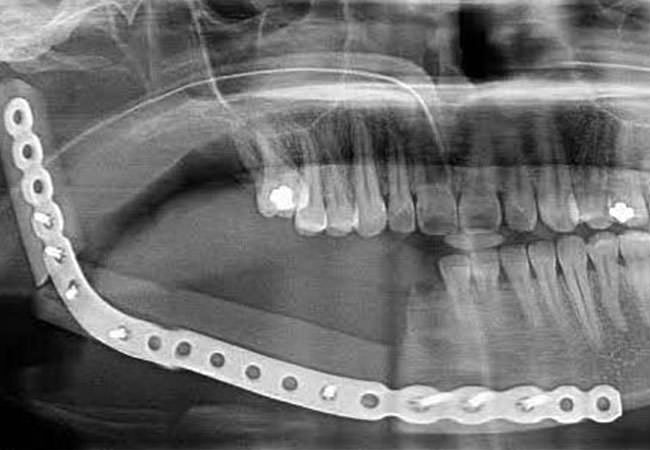
Ameloblastoma - Before
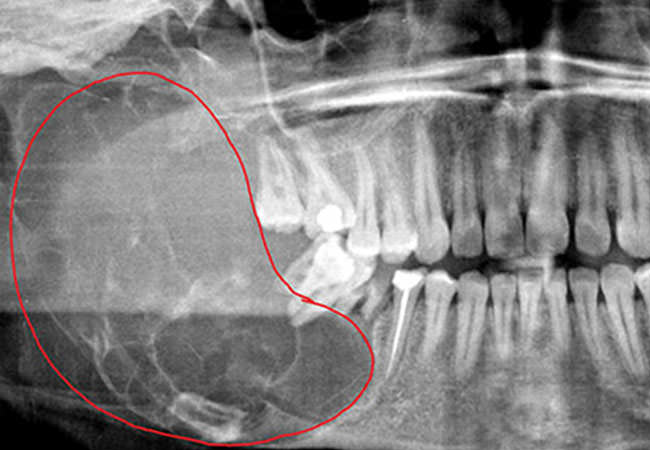
Ameloblastoma - After
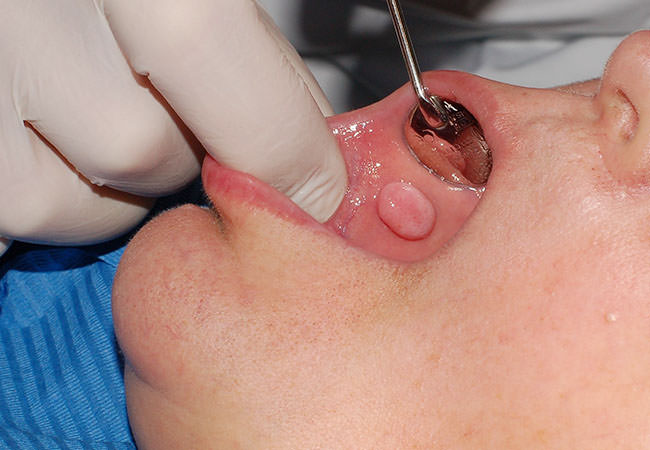
Fibroma
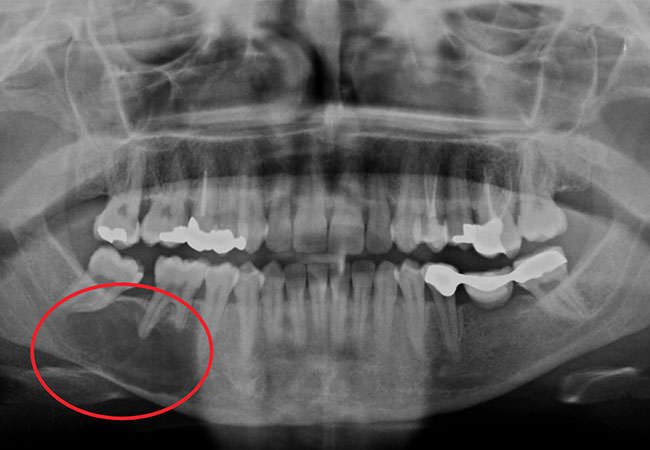
Keratocyst
Nasolabial cyst
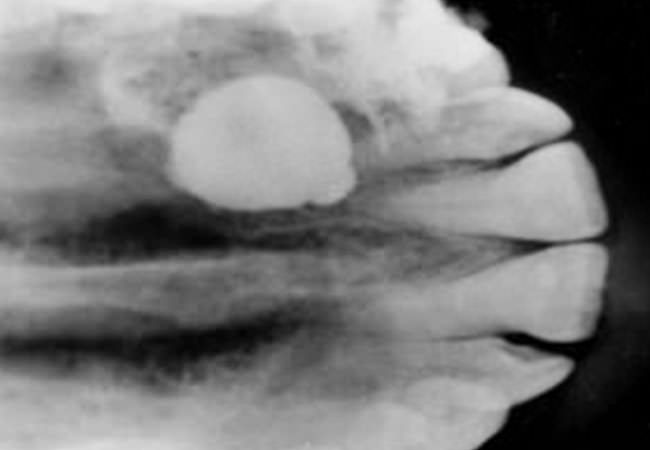
Radicular Cyst - Before
Radicular Cyst - After

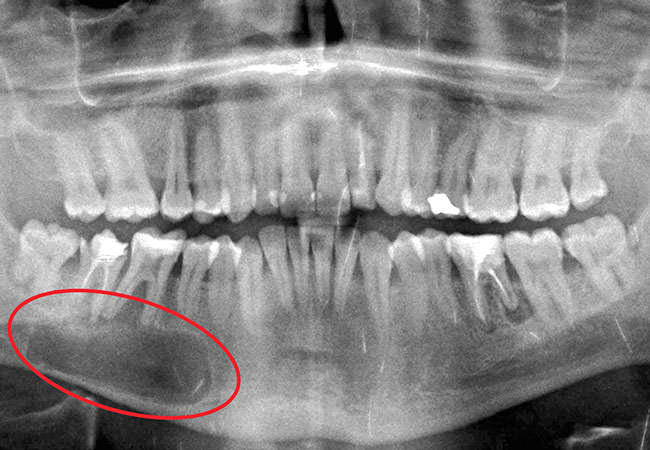
Odontomas
The odontoma may be responsible for blocking the eruption of the maxillary incisors. Are very variable in size, and whether the complex type or compound, its presence is usually preclude the eruption of teeth.
-
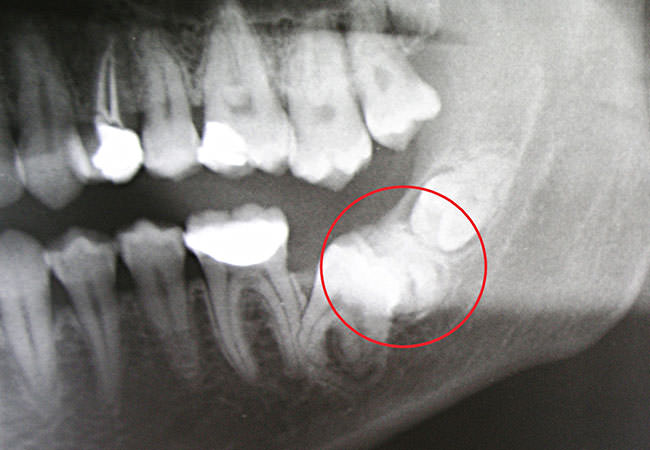
Impacted teeth
An impacted tooth is one that can not erupt (birth), not reaching its position in the dental arch within the expected time. If not removed may bring various problems such as the formation of cysts and tumors. While the teeth that are more frequently impacted are third molars, other teeth may be impacted. The usual procedure for third molar is removal, however other impacted teeth may be removed or exposed and placed in the dental arch.

Why are impacted?
 Why are impacted?
Why are impacted? Lack of space in the dental arch
Lack of space in the dental arch
big teeth Obstacles due to the adjacent tooth or other structure
Obstacles due to the adjacent tooth or other structure Resistance of bone tissue
Resistance of bone tissue Strength of oral mucosa
Strength of oral mucosa Retention of deciduous teeth
Retention of deciduous teeth Premature loss of deciduous teeth by changing the position of permanent
Premature loss of deciduous teeth by changing the position of permanent
Wisdom teeth extraction
Why extract wisdom teeth? Prevention of periodontal disease
Prevention of periodontal disease Prevention of dental caries
Prevention of dental caries Prevent pericoronitis
Prevent pericoronitis Prevention of root resorption
Prevention of root resorption Impacted teeth under dental prostheses
Impacted teeth under dental prostheses Prevention of odontogenic cysts and tumors
Prevention of odontogenic cysts and tumors Avoidance of pain of unknown origin
Avoidance of pain of unknown origin Prevention of fracture of the jaw
Prevention of fracture of the jaw Optimization of periodontal health
Optimization of periodontal healthImpacted wisdom teeth should always be removed?
In most cases yes. Often included teeth / impacted are not treated until some complication to appear, but studies indicate that the wisdom teeth should be removed surgically when the patient is young in order to prevent future problems. .
Where is the surgery performed?
The surgery is performed in an office with local anesthesia.
Traction of impacted teeth - Only the wisdom teeth may be impacted?
No, any teeth may be impacted. The most common are the wisdom teeth and the upper canines and lateral incisors. Impacted teeth, whenever possible, should be relocated in the dental arch. The procedure includes surgical intervention with cementation of bracket in the face of the impacted tooth and its traction for braces previously placed.
-
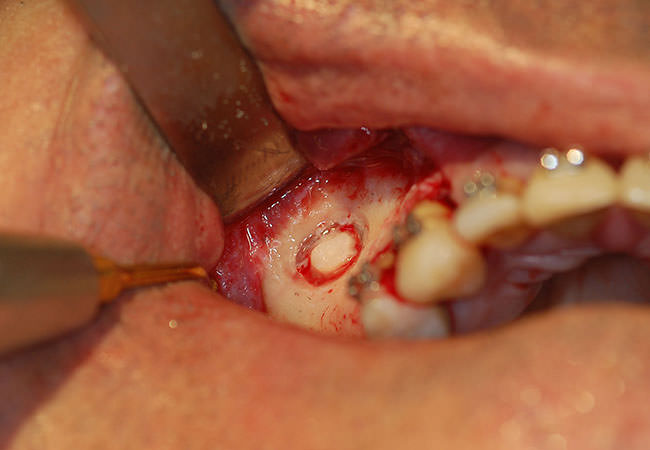
Sinus Lift
This is a surgical procedure that aims to increase bone mass in the jaw in the region of molars and premolars.
When should it be done?
When there is not enough bone in the upper jaw to allow the placement of an implant. The lack of bone in the upper jaw is caused by bone resorption after tooth extraction. Periodontal disease can contribute to greater bone loss. There are individual variations with regard to the size of the maxillary sinus and it's size may increase with age.
Preparation
It's necessary a radiographic exam and computed tomography (CT) to assess the dimensions and shape of the maxillary sinus to prepare the surgery.
How is it done?
First an incision is made in the gum in the region of the premolars, molars and the tissue is raised, exposing the bone. Then a small oval window is opened in the bone.
On the other side of the window is visible the membrane covering the sinus. This membrane is then gently pulled up and the space that was formerly occupied by the sinus is filled with bone graft material. The gum is placed in position and sutured.
How is the post-op?
After surgery, patients typically present some swelling and some loss of blood through the mouth and nose. It is important not to force the nose and avoid sneezing because it may displace the material that was placed inside. It is prescribed medication to control pain, inflammation and prevent infection.
The implants can be placed immediately or after a few months (mean 8 months) after surgery, depending on each case.
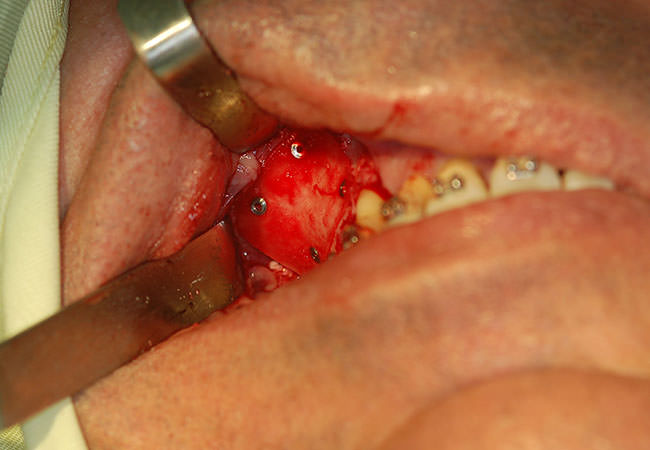
-
Ortho-surgical disjunction of the Palate
Maxillary Expansion
The maxillary expansion can be done basically in four ways:
- Orthopedic disjunction: this kind of disjunction is performed with a dental appliance in patients under 12 years of age with a better effect in the anterior maxilla.
- Orthodontic compensation: also done in adult patients with a maximum gain of 1 mm in each region later. There is a higher dentoalveolar inclination and no bone expansion.
- Orthodontic-Surgical disjunction
- Surgical disjunction does not involve an apparatus on the palate. It is made exclusively with surgery and is reserved for patients who will undergo another type of surgery in the upper jaw beyond that, but the disjunction must be minimized to prevent recurrences..
Ortho-surgical disjunction of the palate
Adult patients with jaw atresia or diminution of the transverse diameter of the upper jaw, should not be treated only with orthodontic disjunction because there will be resistance of the facial skeleton not allowing the palatine bone undergoes expansion. After surgery, the device previously placed is activated fourth round per day and after expansion of the jaw is sealed with resin.
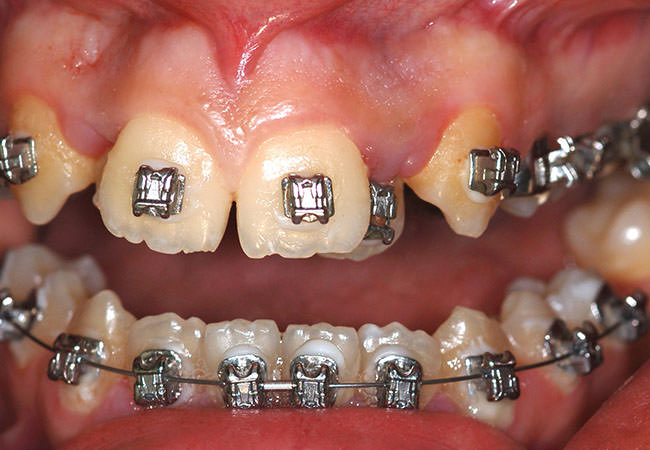
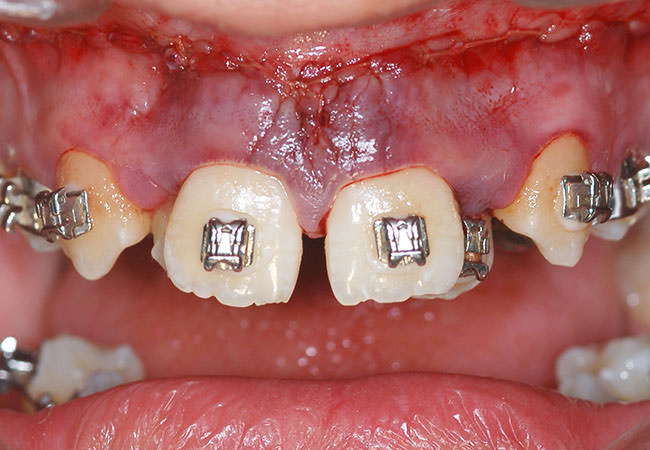
-
Orthognathic surgery
The orthognathic surgery is the treatment for patients who have teeth and skeletal deformities involving the face. When you can not solve the case only with orthodontic treatment, since the problem is in excess or lack of growth of the facial skeleton and not only in position of teeth, then it is necessary orthognathic surgery.
What is the origin of deformities?
These deformities may arise due to Specific Syndromes and Abnormalities (teratogenic factors, embryological factors, hemifacial microsomia, Treacher Collins, facial clefts, cranial synostosis, Pierre Robin ...), disturbances of growth after birth, facial trauma, muscle problems and hormonal or genetic in origin when there is a relative with the same characteristics.
Quais as alterações que podem implicar a necessidade da cirurgia ortognática?
 Difficulty in chewing;
Difficulty in chewing; Difficulty in swallowing;
Difficulty in swallowing; Excessive wear of the teeth;
Excessive wear of the teeth; Open bite;
Open bite; Deep bite;
Deep bite; Crossbite;
Crossbite; Facial disharmony;
Facial disharmony; Birth defects or sequelae of trauma in the face;
Birth defects or sequelae of trauma in the face; Small or retracted chin;
Small or retracted chin; Large or Protuded chin;
Large or Protuded chin; Chin diverted to one side;
Chin diverted to one side; Jaw too far forward or projected;
Jaw too far forward or projected; Jaw too far back or retruded;
Jaw too far back or retruded; Inability to close lips without muscular effort;
Inability to close lips without muscular effort; Mouth breathing;
Mouth breathing; TMJ pain and chronic headaches,
TMJ pain and chronic headaches, Syndrome of obstructive sleep apnea;
Syndrome of obstructive sleep apnea;What are benefits of orthodontic and surgical treatment?
 Improvement of the relationship between the teeth, muscles and skeleton
Improvement of the relationship between the teeth, muscles and skeleton Improvement of breathing
Improvement of breathing Improvement of the positioning of the neck muscles
Improvement of the positioning of the neck muscles Improvement of the positioning of the neck muscles
Improvement of the positioning of the neck muscles Improvement of the positioning of the tongue
Improvement of the positioning of the tongue Improvement of phonation and articulation of words
Improvement of phonation and articulation of words Improvement of occlusion and temporomandibular joint
Improvement of occlusion and temporomandibular joint Improvement of chewing and digestion
Improvement of chewing and digestion Improvement in social relationship
Improvement in social relationshipWhat are the phases of treatment?
 Insertion of fixed appliances - orthodontic treatment can take 18-24 months before the surgery to leave the teeth in a proper position
Insertion of fixed appliances - orthodontic treatment can take 18-24 months before the surgery to leave the teeth in a proper position Orthognathic Surgery-(still with braces)
Orthognathic Surgery-(still with braces) Return to orthodontic treatment after surgery to permanently improve the position of teeth
Return to orthodontic treatment after surgery to permanently improve the position of teethO tempo do tratamento depende do grau de dificuldade do tratamento ortodôntico.
How is the surgery done?
Before the surgery the doctor prepares the surgery with all necessary examinations. The diagnosis and planning of surgery are performed thoroughly before surgery with study models mounted in articulator and cephalometric radiographs. The planning takes much longer than the surgery itself.
The surgery is performed under general anesthetic. The patient is hospitalized on the morning of surgery in "absolute fasting" (can not eat any food nor drink water in 10hrs before surgery) and depending on the situation patients are discharged the next day. The surgery is performed through the oral cavity, leaving no scar on the face. The skeleton is secured with mini titanium plates and screws not allowing micromovement of bones. In post-surgery is normal to appear some swelling which decreases after a few days.
What are the Post-Surgical Care?
 The food should be cold and soft.
The food should be cold and soft. The use of ice decreases the swelling and should be used frequently during the first 24 hours.
The use of ice decreases the swelling and should be used frequently during the first 24 hours. Strict compliance to prescribed medication.
Strict compliance to prescribed medication.Before
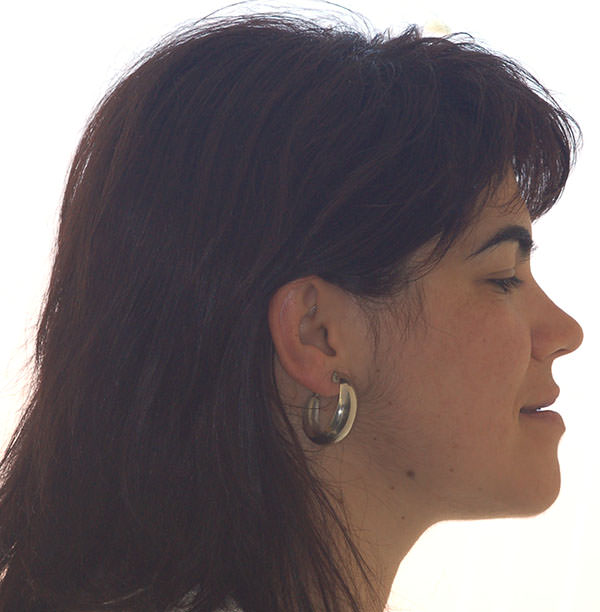

After
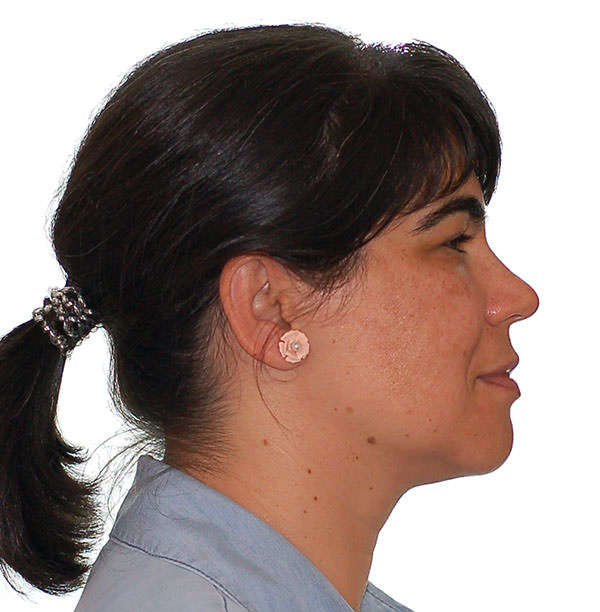

Before
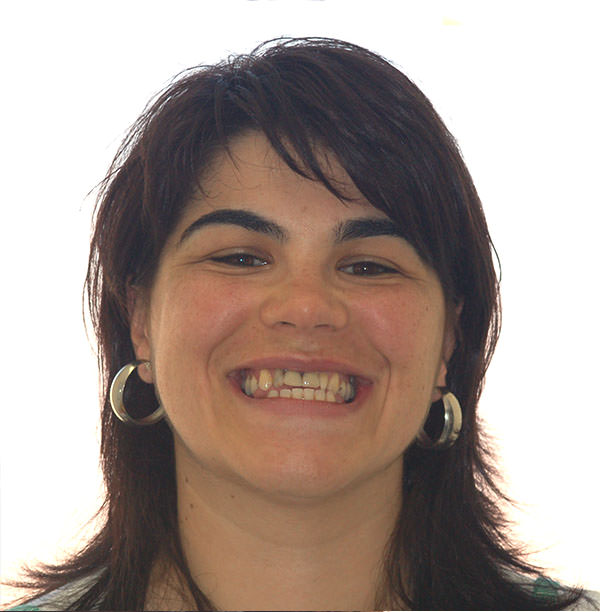

After
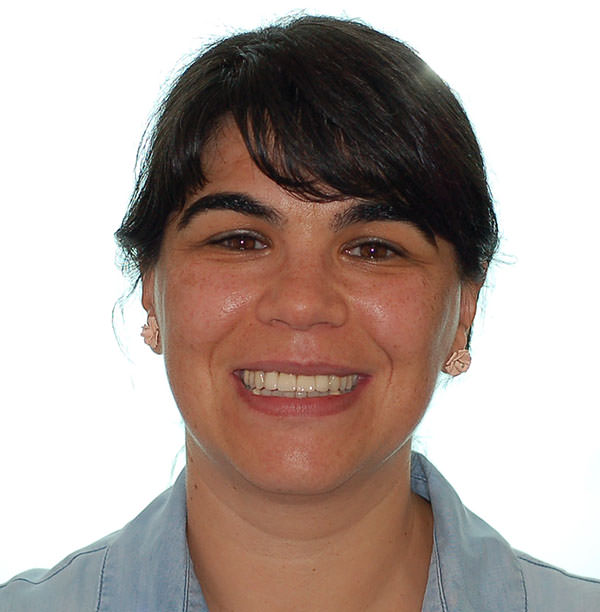

Contacts
-
Calçada de São Lourenço
N.º 3 1.º Andar D
9000-061 Funchal
Opening Hours
-
Monday – Friday
09h00 – 14h00
15h00 – 18h00
Saturdays, Sundays and Holidays
Closed
© Clínica de São Lourenço
Developed by Navega Bem Web Design

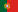
 Case 1
Case 1